Pain Treatments for Cervical and Lumbar Disc Herniation
Cervical and lumbar disc herniation is a condition that occurs when intervertebral discs slip out of place and compress the spinal cord or nerve roots. The resulting pain, numbness, and restricted mobility can significantly impair a patient’s quality of life. Non-surgical treatment of disc herniation encompasses a range of conservative methods aimed at alleviating symptoms in early or moderate stages without the need for surgical intervention. This article reviews the available non-surgical treatment options, the clinical scenarios in which they are preferred, their potential risks and side effects, reported success rates, and key considerations for patients.
What is Non-Surgical Treatment of Disc Herniations?
Non-surgical treatment refers to therapeutic strategies that relieve nerve compression and pain caused by herniated discs without surgical procedures. These approaches aim to reduce mechanical pressure on the affected area of the spine, thereby relieving symptoms such as pain and restricted movement. Conservative methods are typically preferred during the initial stages of herniation but may also be applicable in selected cases of advanced disease.
Common Methods and Stages in Non-Surgical Management
Treatment strategies are chosen based on the severity of herniation, intensity of symptoms, and the patient’s overall health status. Common non-surgical methods include:
- Physical Therapy and Exercise Programs: Physical therapy is one of the most widely used modalities in the treatment of disc herniation. It focuses on strengthening paraspinal muscles, improving flexibility, and reducing axial load on the spine. It is especially effective in early-stage herniations.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: Administering corticosteroids into the epidural space reduces inflammation and alleviates nerve irritation. This intervention is generally reserved for patients with severe pain unresponsive to physical therapy. Although effective in providing temporary relief, it is often used in combination with other modalities for long-term benefits.
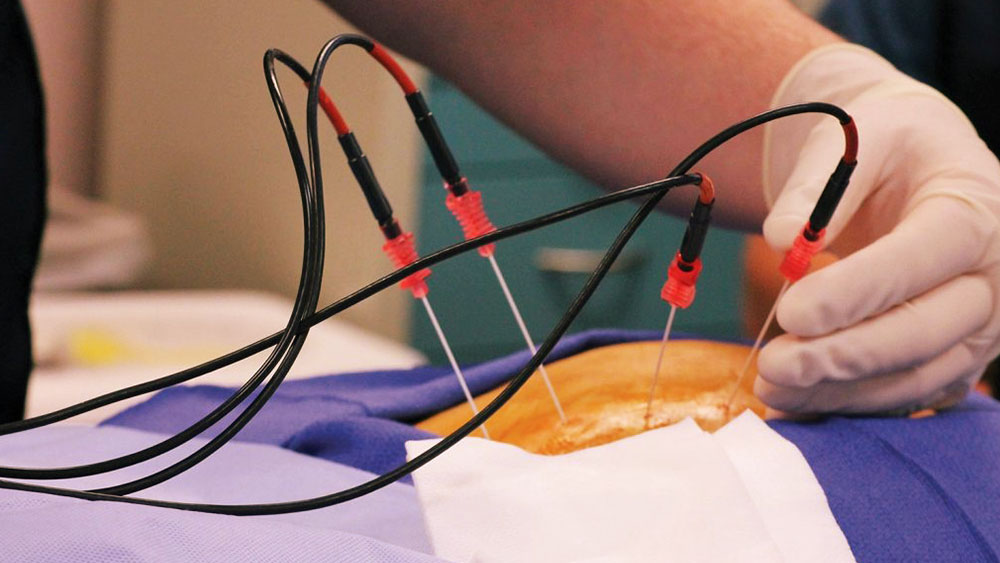
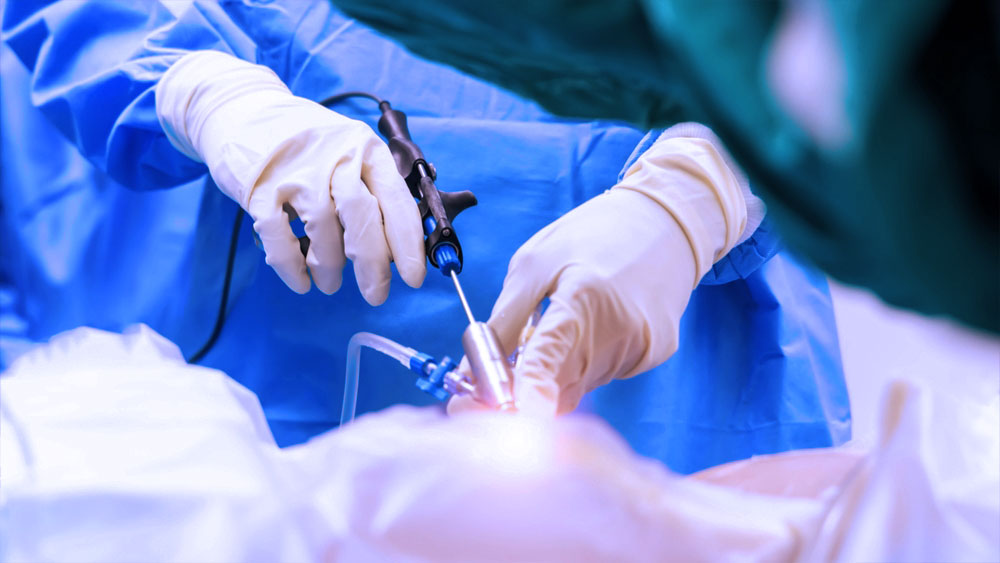
- Radiofrequency (RF) Nerve Ablation: In this minimally invasive procedure, targeted nerve fibers are thermally ablated to interrupt pain signal transmission. RF ablation is typically used in patients with advanced discogenic pain and persistent symptoms.
Applications for Patients with Unsuccessful Surgical Outcomes
Non-surgical treatment may also benefit patients who have undergone disc surgery but continue to experience pain or neurological symptoms. Techniques such as physical therapy, epidural injections, and spinal decompression can be effective in alleviating postoperative discomfort. For these individuals, conservative management helps avoid the risks associated with revision surgery and can improve functional outcomes. Treatment plans in such cases must be customized with consideration for postoperative scar tissue and spinal biomechanics.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Non-Surgical Methods
While generally safe, non-surgical treatments are not without potential complications:
- Physical Therapy and Exercise: Improper techniques or overexertion can exacerbate pain. Supervision by trained professionals is crucial for safety and effectiveness.
- Steroid Injections: Although rare, complications such as infection, bleeding, or nerve injury may occur. Long-term corticosteroid use carries additional risks, so injections are typically limited in frequency.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: Although minimally invasive and generally safe, complications such as infection or unintended nerve damage may occur.
Despite these risks, the overall success rate of non-surgical interventions is favorable, with many patients experiencing meaningful symptom improvement. However, individual response varies, necessitating a personalized treatment approach.
Patient Considerations During and After Treatment
Adherence to medical advice and lifestyle modifications are key to successful outcomes in non-surgical treatment. Patients should pay attention to the following:
- Regular Exercise: Targeted exercises that strengthen core and paraspinal muscles contribute to long-term symptom control. Compliance with prescribed routines is essential.
- Proper Posture and Ergonomics: Maintaining correct sitting posture, particularly for sedentary workers, reduces spinal strain. Ergonomic chairs and regular posture adjustments are recommended.
- Weight Management: Excess weight increases mechanical stress on the lumbar spine. A balanced diet and regular activity are essential for maintaining a healthy body mass index.
- Avoidance of Heavy Lifting: Lifting heavy objects may aggravate the herniation. Patients should avoid such activities, especially during the treatment period.
- Active Lifestyle: Staying physically active promotes spinal health and prevents muscular deconditioning. Light walking and low-impact movement are encouraged.
Non-surgical treatment of disc herniations can effectively relieve symptoms such as pain and limited mobility. Adherence to the treatment plan and adoption of a healthy lifestyle significantly enhance recovery. By following professional guidance, patients can better manage their condition and improve their quality of life.