Cervical Microdiscectomy
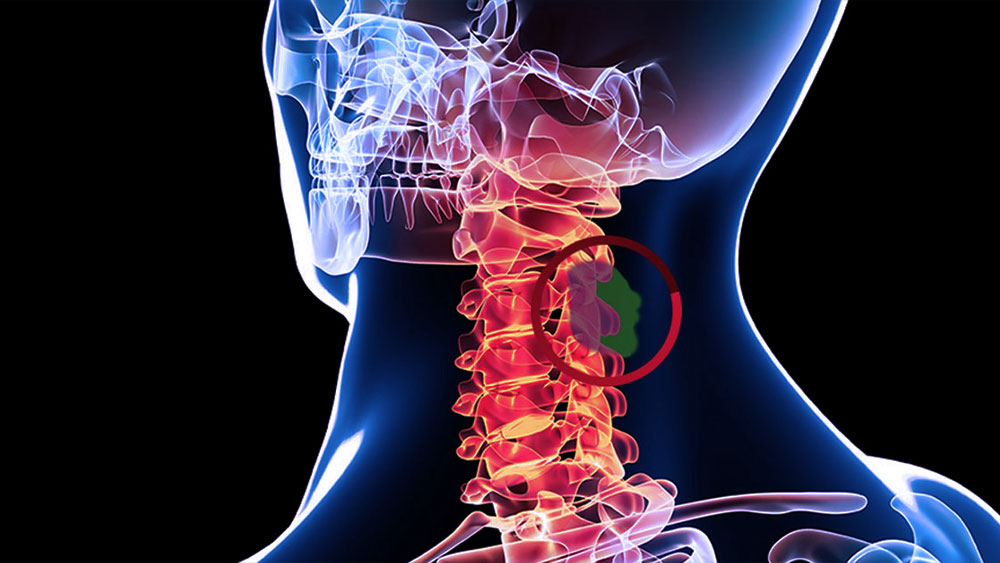
Cervical microdiscectomy is a commonly performed surgical procedure used to address cervical disc herniation-related neck and arm pain. It involves the removal of disc material that is compressing the spinal cord or nerve roots in the cervical spine. This minimally invasive technique aims to relieve neurological symptoms while preserving spinal stability.
Cervical microdiscectomy targets the removal of herniated or degenerative intervertebral discs that cause mechanical compression on nerve structures. Following disc removal, an intervertebral cage or disc prosthesis is inserted to maintain spinal alignment and stability. This method is associated with smaller incisions, reduced soft tissue trauma, and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgeries. It is particularly effective in alleviating symptoms such as cervical radiculopathy and arm weakness due to nerve root impingement.
Before surgery, patients undergo a comprehensive evaluation by a spine specialist who formulates an individualized treatment plan. During surgery, a high-resolution operating microscope is used for precision and safety. Postoperative care includes a period of rest, the use of a cervical collar, and participation in a guided rehabilitation program to facilitate recovery and optimize outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the risks of this procedure?
As with all spinal surgeries, cervical microdiscectomy carries risks including dural tears, bleeding, infection at the surgical site, or nerve injury. However, the procedure is generally safe and well-tolerated when performed by experienced spine surgeons.
- How soon can I return to normal activities after surgery?
The surgery typically lasts 45 minutes to 2 hours. Patients are mobilized within 3–4 hours postoperatively using a cervical collar. Discharge may occur the same evening or the following morning, depending on the patient’s condition. The cervical collar is usually worn for at least two weeks. Light physical activity such as swimming or walking can typically begin after three weeks.
Who is a candidate for this treatment?
This procedure is suitable for patients with cervical disc herniation causing nerve root compression, particularly when conservative treatments have failed.
Are there alternative treatment options?
Yes. In appropriately selected patients, posterior endoscopic (fully minimally invasive) cervical discectomy may be considered. A detailed neurological examination and imaging studies will help determine the best approach.
If you have any questions or wish to schedule an appointment, feel free to contact our team. We are here to support you.
In summary, anterior cervical microdiscectomy is an effective and minimally invasive surgical option for patients suffering from neck and arm pain due to cervical disc pathology.